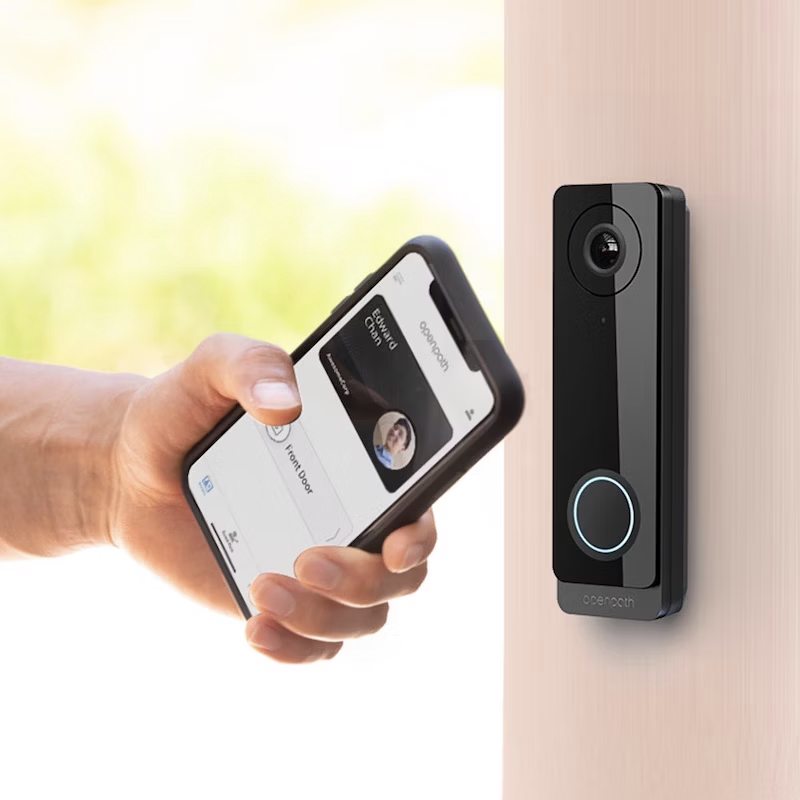

Physical access control systems play an integral role in the protection and management of a property’s security. These systems serve to regulate who can gain entry to certain locations within a facility, thereby safeguarding sensitive areas, protecting assets, and ensuring the safety of personnel. The importance of such systems becomes evident in a world where security threats are varied and can have significant consequences for businesses and institutions alike.
Such systems are not limited to restricting access; they also provide a means of authentication and verification, confirming the identity of individuals before allowing access. This multi-layered approach to security ensures that only authorised personnel can access restricted zones, effectively reducing the likelihood of unauthorised intrusions. The versatility and customisability of modern access control systems allow organisations to tailor security protocols to their specific needs, enhancing overall operational efficiency.
The implementation of physical access control systems facilitates a more streamlined flow of movement for authorised individuals while maintaining a robust security stance. By balancing convenience with security, they enable organisations to operate smoothly without compromising on their protective measures. These systems often contribute to compliance with legal and regulatory standards, ensuring that an organisation meets its due diligence in protecting both data and people.
Physical access control systems are integral to the robust security framework of any organisation, dealing directly with the management of entry to various locations or assets within a facility.
Access control is crucial in safeguarding assets and infrastructure. Organisations leverage physical access control systems to prevent unauthorised entry, ensuring that only authenticated individuals have entry to sensitive zones. Such systems can range from basic lock-and-key setups to sophisticated biometric systems intertwined with access control software, playing a pivotal role in fortifying physical security.
In the context of building site security, physical access control systems are particularly vital. These systems help prevent theft of valuable equipment and materials, ensure only authorised personnel enter potentially hazardous areas, and maintain compliance with health and safety regulations. By implementing robust access control measures, construction companies can significantly reduce risks associated with unauthorised access, ultimately safeguarding their assets and workforce.
The implementation of access control systems importantly contributes to the safety of personnel and compliance with compliance standards. They help in monitoring and controlling the movement of individuals, substantially reducing the risk of occupational hazards and potential security breaches. Ensuring compliance often involves adhering to industry-specific regulations, which an effective access control system can maintain by logging access and generating reports for auditing purposes.
Technology has elevated the effectiveness of access control systems. Today’s physical access control systems often combine hardware with sophisticated software to allow granular control over access rights and real-time monitoring. The integration of technologies such as mobile access, biometrics, and cloud-based access control software tools not only enhances security but also offers convenience and scalability for organisations managing their physical security needs.
Effective physical access control systems are integral to the protection of resources and premises. They operate on principles that identify individuals, verify their credentials, and authorise access based on predefined permissions.
Authentication is the first step in access control, where the system must identify and authenticate an individual. Various authentication methods include something the person has (e.g., key fobs, key cards), something the person knows (e.g., a PIN code), or something that is an inseparable part of the person (e.g., biometric data). Biometric scanners that measure fingerprint scanning, facial recognition, or iris scanning are highly secure as they are unique to each individual and difficult to duplicate.
Once authenticated, the individual’s permissions are checked to authorise access. This authorisation step determines the areas or resources the person can access. These are often defined by role-based access controls that assign different permissions to individuals depending on their job role or status within the organisation.
The physical components and infrastructure form the backbone of access control systems. Essential elements such as locks, keys, turnstiles, gates, card readers, and door locks are installed at access points to physically enforce the authentication and authorisation decisions made by the system. Cabinets and safes might also incorporate these systems to secure sensitive documents or assets.
Physical access control systems often integrate with logical access control systems, which secure networks, computer systems, and applications. An access control server may manage both physical and logical access, ensuring consistency across the systems and enabling comprehensive monitoring and control of various types of entries into the organisation’s environment.
Effective access management and monitoring systems are essential in maintaining security and operational fluency within an organisation. Through precise regulation of access points and real-time monitoring, they ensure that only authorised personnel can enter sensitive areas.
In the realm of physical access control, the visitor and user experience is greatly enhanced by streamlining entry procedures. With technologies like mobile access and QR codes, guests and employees can gain authorised access swiftly and without the cumbersome handling of physical keys. Incorporating visitor management systems that utilise mobile devices can improve convenience for visitors while maintaining strong security protocols.
Surveillance and reporting systems are key components for comprehensive access management. High-definition cameras and video surveillance integrated with control panels allow for constant monitoring of access points. This setup aids in creating an audit trail and reporting anomalies, ensuring a secure environment through meticulous oversight.
Today’s access control solutions employ advanced access technologies to enhance building security. These include biometric authentication, encrypted badges, and mobile credentials that can be managed via smartphones. Such technologies regulate entry more reliably than traditional keys or fobs and help in managing access levels and permissions efficiently. They exemplify how modern access control solutions have adapted to incorporate high-technology features to secure facilities.
To learn more contact our sales team directly sales@mjflood.ie
The necessity for organisations to safeguard their assets and personnel underscores the importance of physical access control. Here, common inquiries are addressed, providing insights into how physical access control bolsters security protocols.
Physical security measures safeguard sensitive areas by restricting access to authorised personnel only. This is critical for preventing unauthorised entry, theft, and ensuring the safety of employees and company assets.
Biometric systems improve physical access control by employing unique biological characteristics, such as fingerprints or iris patterns, for user authentication. This reduces the risk of unauthorised access due to stolen or duplicated traditional credentials.
Best practices include regularly updating access permissions, ensuring that all entry points are covered by access control mechanisms, and integrating physical access control systems with other security solutions for comprehensive coverage.
Physical access control systems are a foundational aspect of cybersecurity, preventing unauthorised persons from physically accessing critical IT infrastructure, which could lead to breaches and data theft.
Devices often used in physical access control include card readers, biometric scanners, electronic locks, turnstiles, and barriers. These devices work in conjunction to secure a facility and manage access effectively.
Examples include keycard systems to manage employee access, biometric authentication for high-security areas, and visitor management systems to track and control guest access within corporate buildings.